Cybercrimes and information security breaches discriminate no one, and the healthcare sector is no exception. With enhanced data storage of health-medical data in recent times on digital-networked devices and cloud storage, there is an enhanced propensity for cybercriminals to be attracted to critical data and information. Instances of cyber-attacks on health care infrastructure are on the rise, according to reports.

The healthcare industry and its services are critical and unavoidable, necessitating payments, debit-credit card linking, sharing of data, personal credentials with hospitals & clinics, medical consultants, physicians, pharmacies to various health care providers including health insurance companies and third-party vendors involved in the medical-health industry.
Cyberattacks targeting medical facilities and sensitive patient information have become increasingly common, endangering the safety and privacy of individuals. Safeguarding healthcare is, therefore, critical, requiring proactive measures to protect its future.
Health care: Top in the list of vulnerable economic sectors
Information security breaches have far-reaching ramifications and dimensions. This is because, unlike other sectors, the sick are live recipients of healthcare services. Protecting their interests is of paramount importance and a constant challenge for governments as well.
The frequency of cyberattacks on the healthcare industry is among the highest. There are several reasons for this: prevalence of legacy IT systems; resource constraints; delayed implementation of robust security protocols and interconnected medical devices lacking adequate built-in security measures. There is a human factor too, at play here, a huge army of medical professionals, who might often inadvertently, fall victim to “social engineering tactics” or engage in unsafe cybersecurity practices due to lack of awareness and training.
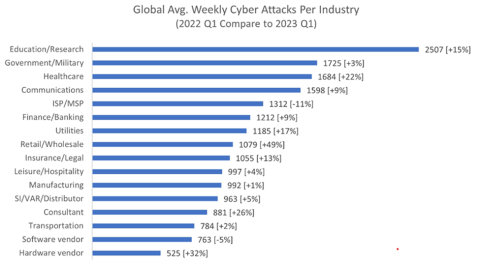
The World Economic Forum reports that health care institutions, particularly hospitals, are a highly vulnerable sector when it comes to cybersecurity breaches. The graph below shows the high vulnerability of the healthcare sector.

Cyber criminals targeting healthcare systems: A snapshot
- Health care systems are goldmines of data of various kinds: financial information, personal data
- “100,000 Plus hospitals: worldwide ( Source: World Hospital Directory: based on geo data: Longitude, Latitude, UTM, GPS, Lombard projection, map, etc)
- Accelerated pace at which digital transformation taking place in health care industry
- Growing startups offering E-health, online consultations, Digital app based medical consultations, remote patient care, etc
- Plethora of linked devices in the digital era
- Role of Robotic interventions in medical field, AI and 5G technology in the sector
- Outsourcing of some of non-core areas of work of the health care industry to outside organizations
- Vendor participation is service delivery of many services within hospital premises
- Huge army of medical professionals and their linked devices connected to storages & clouds
- Medical insurance and involvement of huge chunk of data, personal details in this sector
- Payment and bank account related data
Usual cybersecurity attacks in the healthcare sector
Some of the biggest cybersecurity threats that face this sector are: ransomware attacks, phishing, insider threats, medical device hacking, and unsecured IoT devices. Phishing which involves infecting seemingly innocuous emails with malicious links, where emails look convincing. Ransomware attacks inject malware into a network to infect and encrypt sensitive data until a ransom is paid. These attacks are usually initiated through phishing tactics.
Healthcare providers have seen a growing threat of ransomware attacks. The prevalence of these attacks is due to the healthcare sector’s critical need to maintain operations, making them more likely to pay the ransom to avoid regulatory consequences and patient data theft. Distributed-Denial-of-Service attacks flood a targeted server with fake connection requests, forcing it offline. These attacks often recruit multiple endpoints and IoT devices via malware infections to participate in the coordinated attack.
Challenges and prevention
To safeguard against the growing complexity of cyber threats, healthcare organizations must take proactive measures to prevent incidents. Key steps to reduce the risk include:
- Implementing robust cybersecurity protocols to protect patient data and medical records
- Conducting regular staff training to identify and avoid potential threats
- Enforcing strong access controls and multi-factor authentication to limit unauthorized access, employing advanced monitoring tools for real-time detection of anomalies
- Regularly updating software and devices to minimize vulnerabilities, adopting a zero trust approach to reduce the attack surface
- Addressing third-party security risks through assessments and vendor tiering
- Promoting cyber threat awareness among staff through webinars and resources
- Enabling multi-factor authentication on endpoints and mobile devices for added security against cyber-attacks. By following these measures, healthcare institutions can strengthen their defences and safeguard patient information in an increasingly digital landscape.
The healthcare industry faces escalating cyber threats due to its vast data repositories and digital transformation. Cyberattacks targeting medical facilities and patient information have become common, posing serious risks to individual safety and privacy. Proactive measures such as robust cybersecurity protocols, staff training and multi-factor authentication, are crucial to secure the future of healthcare.





