By adopting a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, financial institutions can effectively protect their systems, safeguard sensitive customer data, and maintain their role as the backbone of our economies. Tahawultech examines.

The array of options in digital payment systems has ushered in a realm of unprecedented convenience for everyone. Yet, the increasing prevalence of transaction options in this medium necessitates caution and the implementation of measures to ensure the security of our payments and data.
Digital payments and transactions have taken center stage as the global digital economy rapidly expands. The total digital transaction value is expected to demonstrate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.52% from 2024 to 2028, reaching a projected total of US$16.62 trillion by 2028(Source: Statista).
The acceleration of digital payment growth is influenced by various factors, including the seamless and rapid transaction capabilities of digital infrastructure. The significant surge in digital transformation at the enterprise level, coupled with the expansion of e-commerce and online marketplaces, further propels this trend. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has played a pivotal role in expediting the widespread adoption of digital payments. While businesses have compelling financial reasons to embrace digital transactions, it is imperative that they comprehend the primary security risks associated with such transactions. Implementing appropriate protocols is crucial to mitigating these risks, safeguarding both the businesses and their customers. This proactive approach enables businesses to harness the benefits of digital payments while ensuring the enduring viability of customer relationships in the long term.
Transaction Methods
Financial transactions and related services transcend geographical boundaries, harnessing the immense power of digital technologies and increasingly embracing cloud-based infrastructure. Trillions of messages and signals traverse this intricate network of connected servers every minute, orchestrating a symphony of financial transactions. ATM withdrawals, bank transfers, retail payments, shopping transactions, money transfers, and e-commerce payments all contribute to this intricate web of interconnected networks. Digital wallets, debit and credit cards, account numbers and personal data form the bedrock of these transactions.
The banking and financial sectors’ role extends beyond mere transaction facilitation; they serve as catalysts for economic growth and stability. By channeling funds from savers to borrowers, banks and financial institutions enable businesses to invest, expand operations, and create employment opportunities. This cyclical process of financial intermediation fuels economic growth and prosperity.
However, the very interconnectedness and digital nature of the banking and financial sectors render them vulnerable to a barrage of cyber threats. Data breaches, ransomware attacks and sophisticated phishing schemes pose a constant threat to the integrity of financial systems and the confidentiality of sensitive customer information. The potential consequences of such cyber incidents extend far beyond financial losses; they can erode customer trust, disrupt financial markets, and undermine the overall stability of the economy.
With growing digitalization, internet access, mobile & e-wallets, the world is about to witness a major revolution in digital payment systems.
Number of cashless transactions worldwide
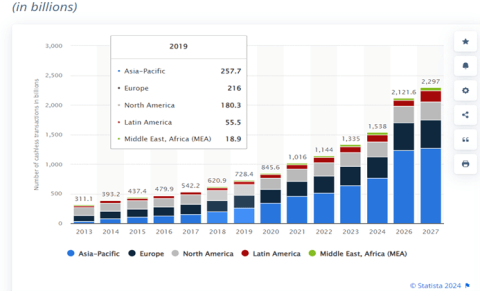
Financial transactions are becoming increasingly cashless globally, they play a vital role in the entire gamut of infrastructure that constitutes the digital economy. This calls for attention to the question of security in this this crucial arm of the digital economy.
Multipronged approach: cyberthreats
To safeguard the banking and financial sector from the onslaught of cyber threats, a multi-pronged approach is essential. Robust cybersecurity frameworks, encompassing layered defense mechanisms, continuous security updates and comprehensive employee training programs, are crucial to shield financial institutions from cyberattacks. Additionally, data loss prevention (DLP) solutions can serve as a valuable tool, monitoring and controlling data access, usage, and sharing to prevent unauthorized data exfiltration.
Protecting data and information in this sector are vital for several reasons:
- Maintaining customer trust: Customers entrust their personal and financial information to banks and financial institutions. A data breach can erode this trust, leading to customer churn, damage to the institution’s reputation, and potential legal and regulatory repercussions.
- Preventing financial losses: Data breaches can result in significant financial losses for both banks and their customers. Stolen financial information can be used for fraudulent transactions, identity theft, and other criminal activities.
- Ensuring financial stability: The financial sector is a critical component of the global economy. A large-scale data breach could disrupt financial markets and have a domino effect on other industries.
Key Challenges in Data Security
The banking and financial sector faces several unique challenges in protecting data and information:
- Complexity of systems: Financial institutions often have complex IT infrastructures that include legacy systems, new applications, and third-party integrations. This complexity makes it difficult to implement and maintain consistent security controls across the entire environment.
- Vast amounts of data: Banks and financial institutions collect and store vast amounts of sensitive data, including customer information, financial transactions, and proprietary intellectual property. This large volume of data makes it difficult to identify and protect against potential threats.
- Evolving cyber threats: Cybercriminals are constantly developing new and sophisticated methods for attacking financial systems. Banks and financial institutions must continuously adapt their security strategies to stay ahead of these threats.
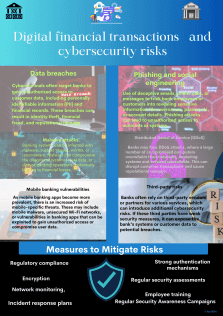
Strategies for Effective Data Security
To effectively protect data and information, banks and financial institutions must adopt a comprehensive approach to security that includes the following strategies:
- Implement a layered security architecture: A layered security architecture includes multiple layers of protection, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption, to make it more difficult for attackers to penetrate a system.
- Regularly update software and systems: Software vulnerabilities are often exploited by cybercriminals. Banks and financial institutions should maintain a regular patching schedule to ensure that their systems are up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Educate employees about cybersecurity: Employees are often the weakest link in the security chain. Banks and financial institutions should provide regular security awareness training to their employees to help them identify and avoid cyber threats.
- Implement a data loss prevention (DLP) solution: A DLP solution can help prevent sensitive data from being leaked or stolen by monitoring and controlling how data is accessed, used, and shared.
- Continuously monitor and audit security systems: Banks and financial institutions should continuously monitor their security systems for signs of intrusion or suspicious activity. They should also conduct regular security audits to identify and address any vulnerabilities.
By implementing these strategies, banks and financial institutions can significantly reduce their risk of data breaches and protect the sensitive information that is vital to their operations and the overall stability of the financial system.
The banking and financial sector stands as a pillar of economic vitality, facilitating the transactions that drive economic growth and prosperity. However, the sector’s digital transformation and interconnectedness expose it to a range of cyber threats. By adopting a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, financial institutions can effectively protect their systems, safeguard sensitive customer data, and maintain their role as the backbone of our economies.